(Peer-Reviewed) Streamlined photonic reservoir computer with augmented memory capabilities
Changdi Zhou 周长笛 ¹ ², Yu Huang 黄于 ¹ ², Yigong Yang 杨一功 ¹ ², Deyu Cai 蔡德宇 ¹ ², Pei Zhou 周沛 ¹ ², Kuenyao Lau 刘坤耀 ¹ ², Nianqiang Li 李念强 ¹ ², Xiaofeng Li 李孝峰 ¹ ²
¹ School of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering & Collaborative Innovation Center of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, China
中国 苏州 苏州大学光电科学与工程学院 苏州纳米科技协同创新中心
² Key Lab of Advanced Optical Manufacturing Technologies of Jiangsu Province & Key Lab of Modern Optical Technologies of Education Ministry of China, Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, China
中国 苏州 苏州大学 江苏省先进光学制造技术重点实验室 教育部现代光学技术重点实验室
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2024-10-22
Abstract
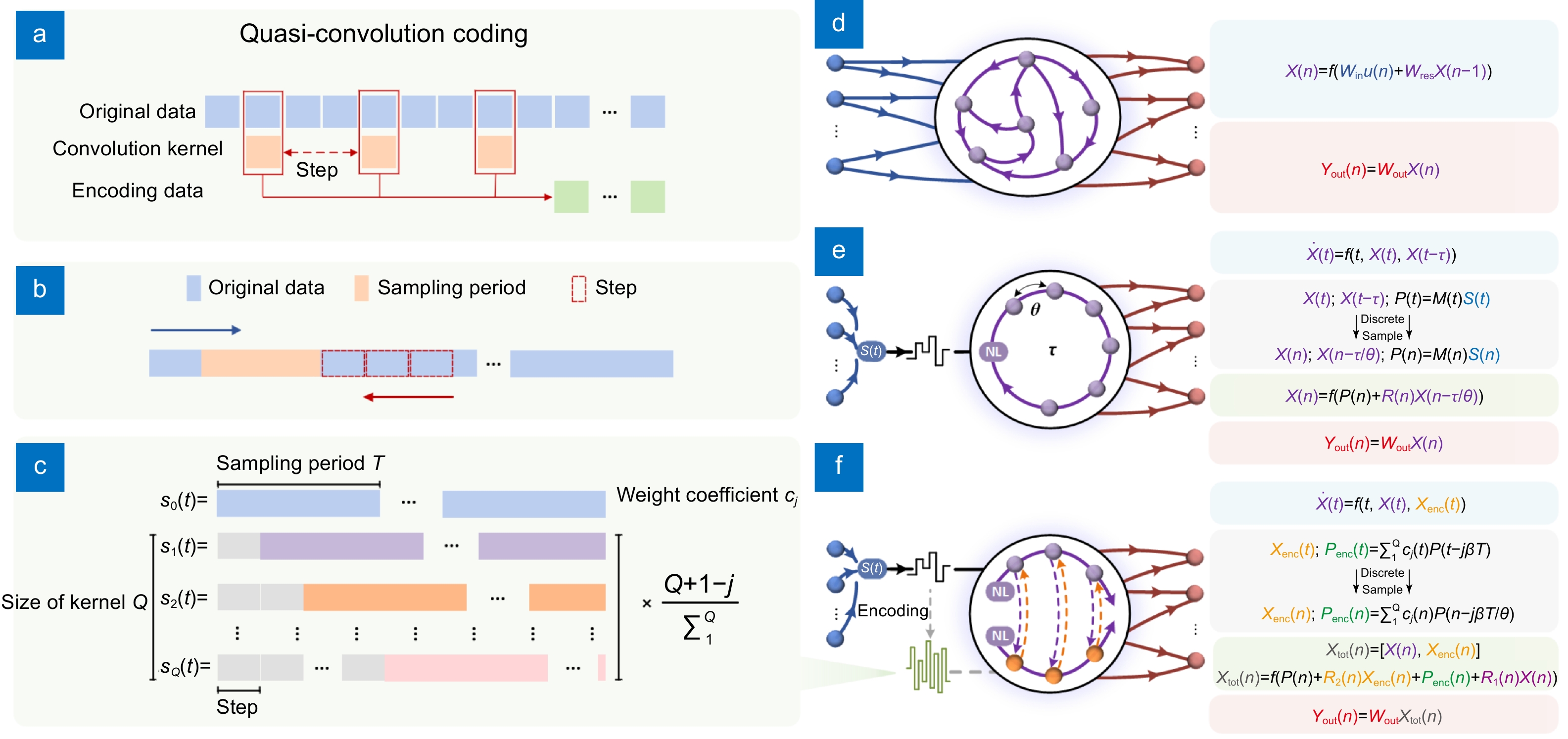
Photonic platforms are gradually emerging as a promising option to encounter the ever-growing demand for artificial intelligence, among which photonic time-delay reservoir computing (TDRC) is widely anticipated. While such a computing paradigm can only employ a single photonic device as the nonlinear node for data processing, the performance highly relies on the fading memory provided by the delay feedback loop (FL), which sets a restriction on the extensibility of physical implementation, especially for highly integrated chips.
Here, we present a simplified photonic scheme for more flexible parameter configurations leveraging the designed quasi-convolution coding (QC), which completely gets rid of the dependence on FL. Unlike delay-based TDRC, encoded data in QC-based RC (QRC) enables temporal feature extraction, facilitating augmented memory capabilities. Thus, our proposed QRC is enabled to deal with time-related tasks or sequential data without the implementation of FL.
Furthermore, we can implement this hardware with a low-power, easily integrable vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser for high-performance parallel processing. We illustrate the concept validation through simulation and experimental comparison of QRC and TDRC, wherein the simpler-structured QRC outperforms across various benchmark tasks. Our results may underscore an auspicious solution for the hardware implementation of deep neural networks.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25