(Peer-Reviewed) Towards the performance limit of catenary meta-optics via field-driven optimization
Siran Chen ¹ ² ³, Yingli Ha 哈颖丽 ¹ ² ⁴, Fei Zhang 张飞 ¹ ², ⁴, Mingbo Pu 蒲明博 ¹ ² ³ ⁴, Hanlin Bao 包汉霖 ¹ ² ³, Mingfeng Xu 徐明峰 ¹ ² ⁴, Yinghui Guo 郭迎辉 ¹ ² ³ ⁴, Yue Shen ⁵, Xiaoliang Ma 马晓亮 ¹ ² ³, Xiong Li 李雄 ¹ ² ³, Xiangang Luo 罗先刚 ¹ ²
¹ National Key Laboratory of Optical Field Manipulation Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
中国 成都 中国科学院 光场调控科学技术全国重点实验室
² State Key Laboratory of Optical Technologies on Nano-Fabrication and Micro-Engineering, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
中国 成都 中国科学院光电技术研究所 微细加工光学技术国家重点实验室
³ College of Materials Science and Opto-Electronic Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
中国 北京 中国科学院大学 材料科学与光电技术学院
⁴ Research Center on Vector Optical Fields, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
中国 成都 中国科学院光电技术研究所矢量光场研究中心
⁵ Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of California Los Angeles (UCLA), Los Angeles, California 90095, USA
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2024-01-31
Abstract
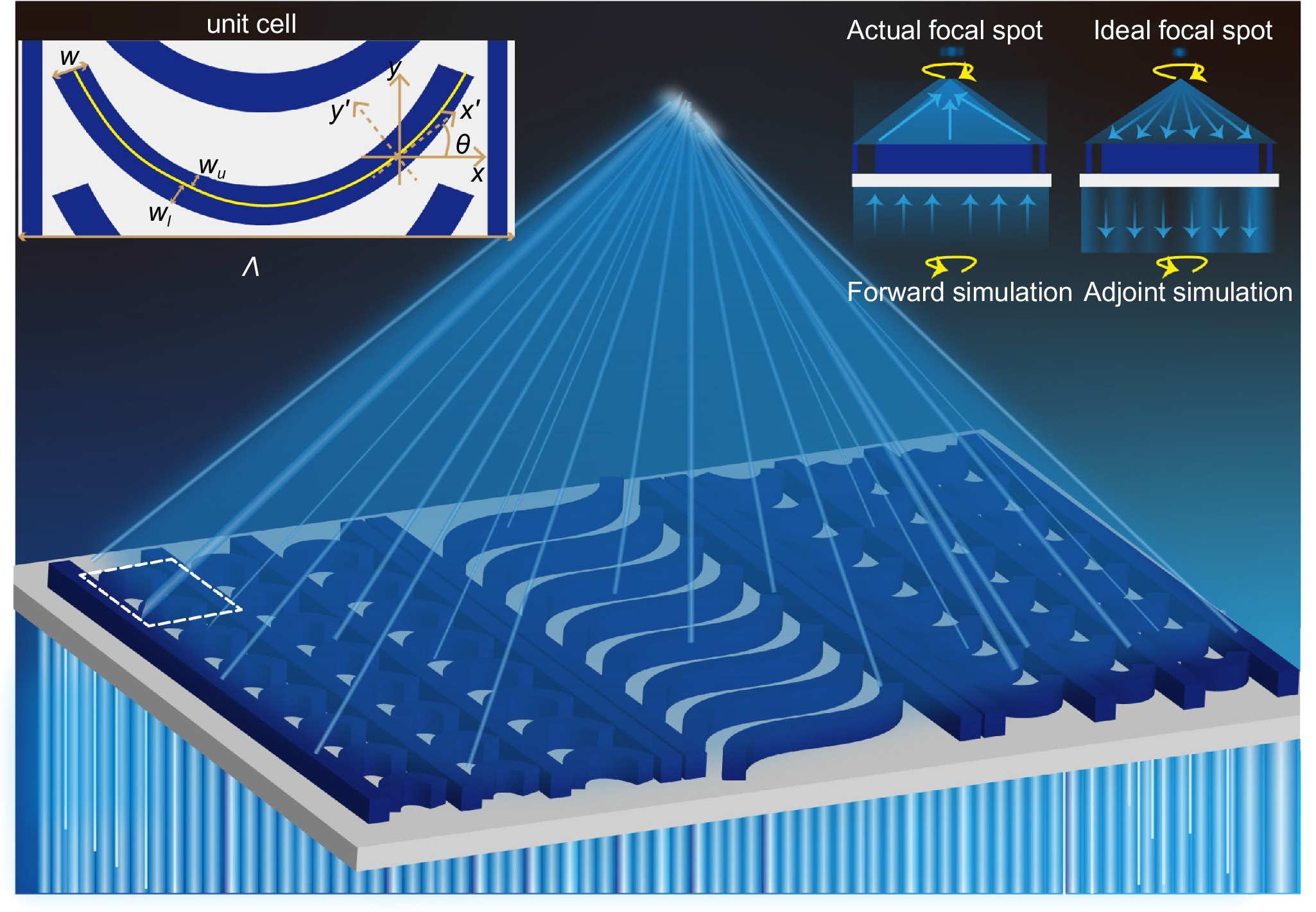
Catenary optics enables metasurfaces with higher efficiency and wider bandwidth, and is highly anticipated in the imaging system, super-resolution lithography, and broadband absorbers. However, the periodic boundary approximation without considering aperiodic electromagnetic crosstalk poses challenges for catenary optical devices to reach their performance limits.
Here, perfect control of both local geometric and propagation phases is realized through field-driven optimization, in which the field distribution is calculated under real boundary conditions. Different from other optimization methods requiring a mass of iterations, the proposed design method requires less than ten iterations to get the efficiency close to the optimal value. Based on the library of shape-optimized catenary structures, centimeter-scale devices can be designed in ten seconds, with the performance improved by ~15%.
Furthermore, this method has the ability to extend catenary-like continuous structures to arbitrary polarization, including both linear and elliptical polarizations, which is difficult to achieve with traditional design methods. It provides a way for the development of catenary optics and serves as a potent tool for constructing high-performance optical devices.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25