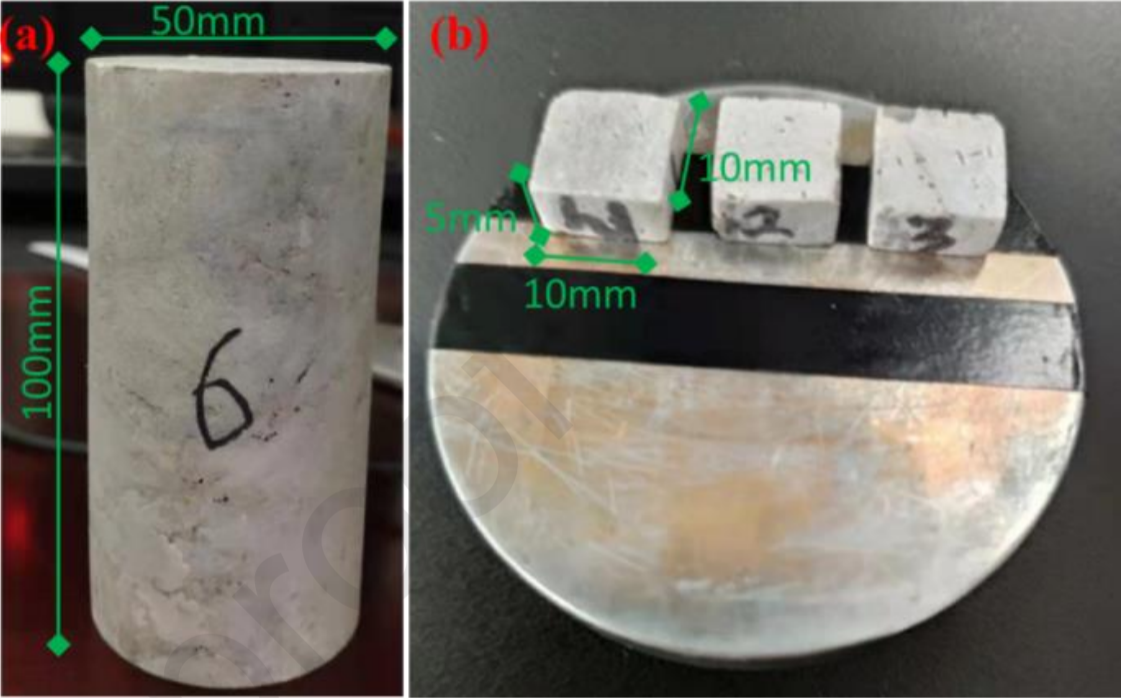
(Peer-Reviewed) Experimental studies on the pore structure and mechanical properties of anhydrite rock under freeze-thaw cycles
Chao Hou 候超 ¹, Xiaoguang Jin 靳晓光 ¹ ² ³, Jie He 何洁 ¹, Hanlin Li 李翰林 ¹
¹ School of Civil Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400045, China
中国 重庆 重庆大学土木工程学院
² Key Laboratory of New Technology for Construction of Cities in Mountain Area of the Ministry of Education, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400045, China
中国 重庆 重庆大学 山地城镇建设与新技术教育部重点实验室
³ State Key Laboratory of Coal Mine Disaster Dynamics and Control, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400045, China
中国 重庆 重庆大学 煤矿灾害动力学与控制国家重点实验室
Abstract
To study the deterioration mechanisms of anhydrite rock under the freeze-thaw weathering process, the physico-mechanical characteristics and microstructure evolutions of anhydrite samples were determined by a series of laboratory tests. Then, a descriptive-behavioral model was used to measure the integrity loss in anhydrite samples caused by cyclic freeze-thaw. Finally, the freeze-thaw damage mechanisms of anhydrite rock were revealed from the macro and micro aspects.
The results show that the pore size of the anhydrite rock is mainly concentrated in the range of 0.001–10 μm. As the number of freeze-thaw cycles increases, there is a growth in the proportion of macropores and mesopores. However, the proportion of micropores shows a declining trend. The relations of the uniaxial compressive strength, triaxial compressive strength, cohesion, and elastic modulus versus freeze-thaw cycles can be fitted by a decreasing exponential function, while the internal friction angle is basically unchanged with freeze- thaw cycles. With the increase of confining pressure, the disintegration rates of the compressive strength and the elastic modulus decrease, and the corresponding half-life values increase, which reveals that the increase of confining pressures could inhibit freeze-thaw damage to rocks.
Moreover, it has been proven that the water chemical softening mechanism plays an essential role in the freeze-thaw damage to anhydrite rock. Furtherly, it is concluded that the freeze-thaw weathering process significantly influences the macroscopic and microscopic damages of anhydrite rock.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25