(Peer-Reviewed) Customized anterior segment photoacoustic imaging for ophthalmic burn evaluation in vivo
Huangxuan Zhao 赵煌旋 ¹ ² ³, Ke Li 李珂 ² ³ ⁴, Fan Yang 杨帆 ¹, Wenhui Zhou ¹, Ningbo Chen 陈宁波 ², Liang Song 宋亮 ², Chuansheng Zheng 郑传胜 ¹, Zhicheng Liu 刘志成 ³ ⁴, Chengbo Liu 刘成波 ²
¹ Department of Radiology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022 China
中国 武汉 华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院放射科
² Research Laboratory for Biomedical Optics and Molecular Imaging, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy ofSciences, Shenzhen 518055, China
中国 深圳 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 生物医学光学与分子影像研究室
³ School of Biomedical Engineering, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China
中国 北京 首都医科大学生物医学工程学院
⁴ Beijing KeyLaboratory of Fundamental Research on Biomechanics in Clinical Application, Beijing 100069, China
中国 北京 临床生物力学应用基础研究北京市重点实验室
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2021-06-20
Abstract
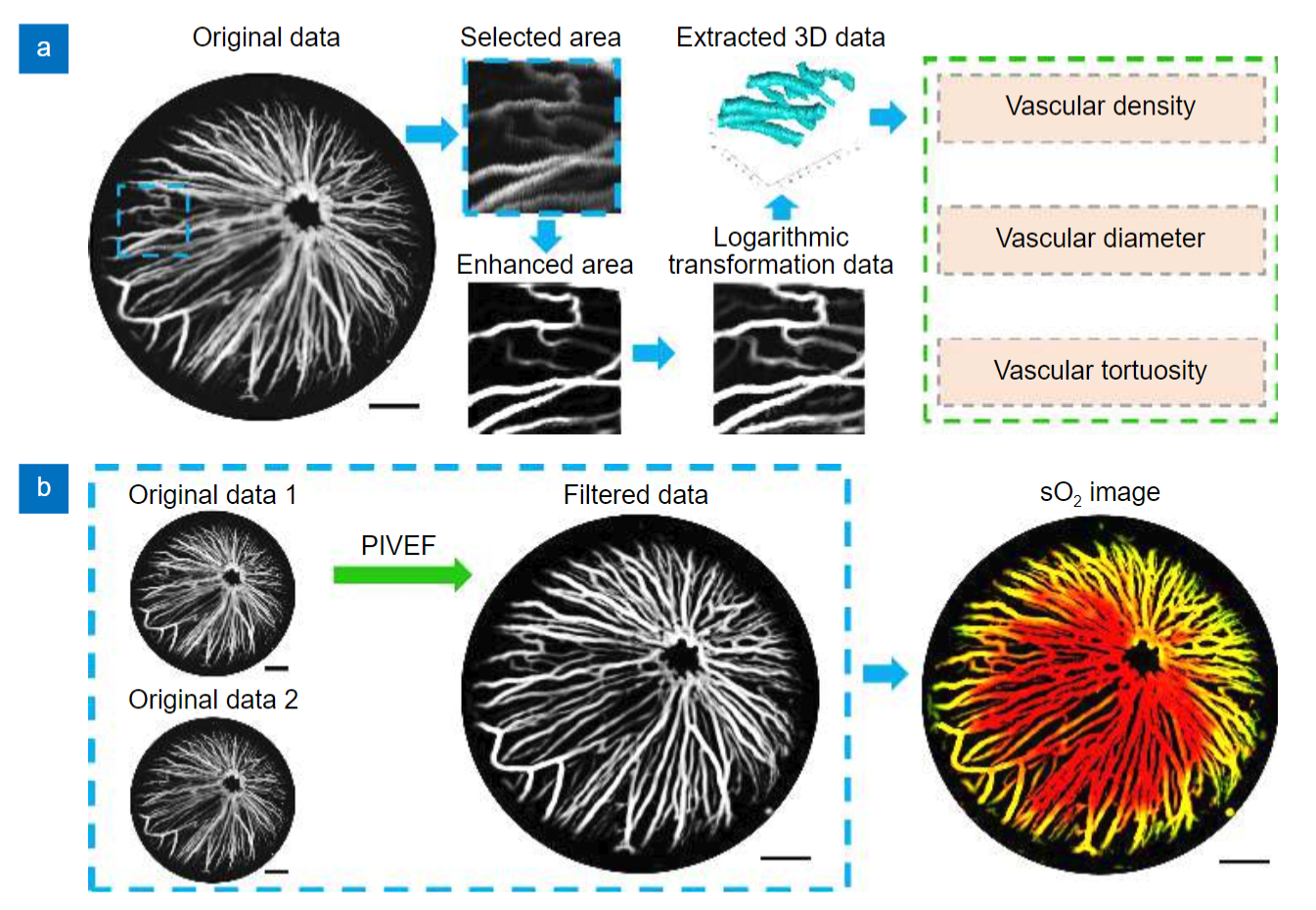
Photoacoustic imaging has many advantages in ophthalmic application including high-resolution, requirement of no exogenous contrast agent, and noninvasive acquisition of both morphologic and functional information. However, due to the limited depth of focus of the imaging method and large curvature of the eye, it remains a challenge to obtain high quality vascular image of entire anterior segment.
Here, we proposed a new method to achieve high quality imaging of anterior segment. The new method applied a curvature imaging strategy based on only one time scanning, and hence is time efficient and more suitable for ophthalmic imaging compared to previously reported methods using similar strategy. A custom-built photoacoustic imaging system was adapted for ophthalmic application and a customized image processing method was developed to quantitatively analyze both morphologic and functional information in vasculature of the anterior segment.
The results showed that the new method improved the image quality of anterior segment significantly compared to that of conventional high resolution photoacoustic imaging. More importantly, we applied the new method to study ophthalmic disease in an in vivo mouse model for the first time. The results verified the suitability and advantages of the new method for imaging the entire anterior segment and the numerous potentials of applying it in ophthalmic imaging in future.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25