(Peer-Reviewed) Calcium hydride reduced high-quality Nd–Fe–B powder from Nd–Fe–B sintered magnet sludge
Haibo Xu 徐海波 ¹, Qingmei Lu 路清梅 ¹ ², Liying Cong ¹, Haowen Tian ¹, Weiqiang Liu 刘卫强 ¹ ², Youhao Liu 刘友好 ² ³, Yunqiao Wang ⁴, Jingwu Chen 陈静武 ² ³, Xiaofei Yi 衣晓飞 ² ³, Ming Yue 岳明 ¹ ²
¹ Key Lab of Advanced Functional Materials, Ministry of Education, Faculty of Materials and Manufacturing, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing, 100124, China
中国 北京 北京工业大学 材料科学与工程学院 新型功能材料教育部重点实验室
² State Key Laboratory of Rare Earth Permanent Magnetic Materials, Hefei 231500, China
中国 合肥 稀土永磁材料国家重点实验室
³ Earth–Panda Advanced Magnetic Materials Co., Ltd., Hefei 231500, China
中国 合肥 安徽大地熊新材料股份有限公司
⁴ Beijing Zhong Ke San Huan Research, Beijing 102200, China
中国 北京 中科三环研究院
Abstract
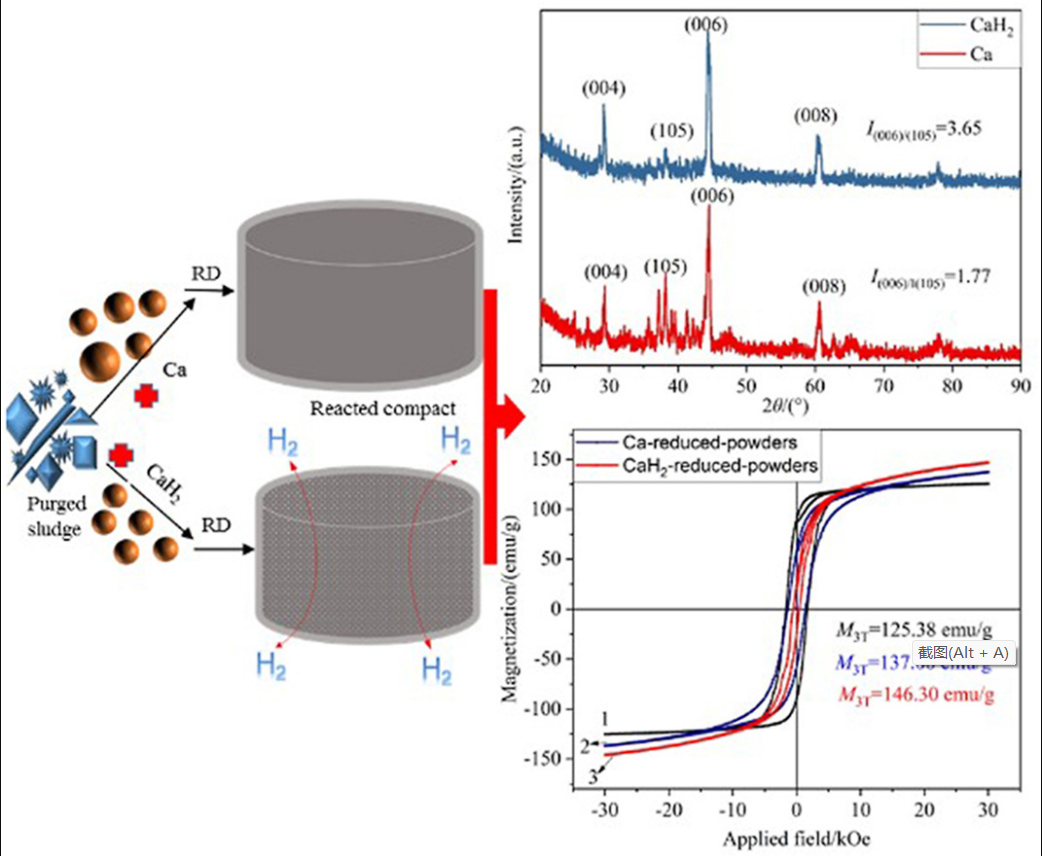
The structural and magnetic properties were studied for recycling Nd–Fe–B powders from Nd–Fe–B sintered magnets sludge via reduction diffusion (RD) with calcium hydride (CaH2) particles. For comparison, traditional reducing agent calcium granules were applied to prepare recycled Nd–Fe–B powders. Finer particle size and better size distribution as well as lower impurity content are achieved by using CaH2 instead of Ca. In detail, the average particle size of the recycled Nd–Fe–B powder is reduced from 4.66 to 3.43 μm, and the bimodal distribution disappears. Moreover, the residual calcium content and oxygen content are reduced to about 0.080 wt% and 0.32 wt%.
As a consequence, the room-temperature magnetization of the CaH2-recycled Nd–Fe–B powder is increased to 146.30 emu/g, 6.8% and 33%, respectively, higher than that of Ca-reduced powder and the initial sludge. Further analysis indicates that CaH2 is able to reduce the sludge at lower temperature to fabricate well-dispersed, uniform recycled powder with high magnetization arising from a combination factors of its low melting point, low thermodynamic behavior, and the release of hydrogen during the reaction.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25