(Peer-Reviewed) Liquid vortexes and flows induced by femtosecond laser ablation in liquid governing formation of circular and crisscross LIPSS
Dongshi Zhang 张东石 ¹ ², Xinzhuo Li ³, Yao Fu ³, Qinghe Yao 姚清河 ³, Zhuguo Li 李铸国 ¹ ⁴, Koji Sugioka ²
¹ Shanghai Key Laboratory of Materials Laser Processing and Modification, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
中国 上海 上海交通大学材料科学与工程学院 上海市激光制造与材料改性重点实验室
² RIKEN Center for Advanced Photonics, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako, Saitama 351-0198, Japan
³ School of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China
中国 广州 中山大学航空航天学院
⁴ State Key Lab of Metal Matrix Composites, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
中国 上海 上海交通大学材料科学与工程学院 金属基复合材料国家重点实验室
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2022-02-28
Abstract
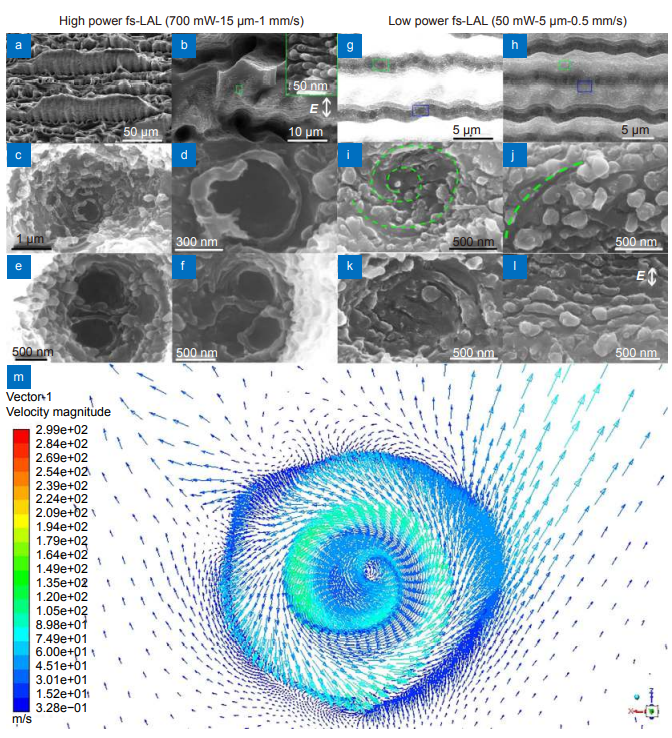
Orientations of laser induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS) are usually considered to be governed by the laser polarization state. In this work, we unveil that fluid dynamics induced by femtosecond (fs) laser ablation in liquid (fs-LAL) can easily break this polarization restriction to produce irregular circular-LIPSS (CLIPPS) and crisscross-LIPSS (CCLIPSS). Fs laser ablation of silicon in water shows formation of diverse LIPSS depending on ablation conditions.
At a high power of 700 mW (repetition rate of 100 kHz, pulse duration of 457 fs and wavelength of 1045 nm), single/twin CLIPSS are produced at the bottom of macropores of several microns in diameter due to the formation of strong liquid vortexes and occurrence of the vortex shedding effect. Theoretical simulations validate our speculation about the formation of liquid vortex with an ultrahigh static pressure, which can induce the microstructure trenches and cracks at the sidewalls for fs-LAL of Si and tungsten (W) in water, respectively. At a low power of 50 mW, weak liquid vortexes are produced, which only give birth to curved LIPSS in the valleys of grooves.
Consequently, it is deduced that liquid vortex plays a crucial role in the formation of macropores. Mountain-like microstructures induce complex fluid dynamics which can cause the formation of CCLIPSS on them. It is believed that liquid vortexes and fluid dynamics presented in this work open up new possibilities to diversify the morphologies of LIPSS formed by fs-LAL.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25