(Peer-Reviewed) Radical SAM-Dependent Demetallation of Heme
Jinduo Cheng 程金铎 ¹, Wei Ding 丁伟 ², Qi Zhang 张琪 ¹
¹ Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200433 China
中国 上海 复旦大学化学系
² State Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism, School of Life Sciences & Biotechnology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 China
中国 上海 上海交通大学生命科学技术学院 微生物代谢国家重点实验室
Abstract
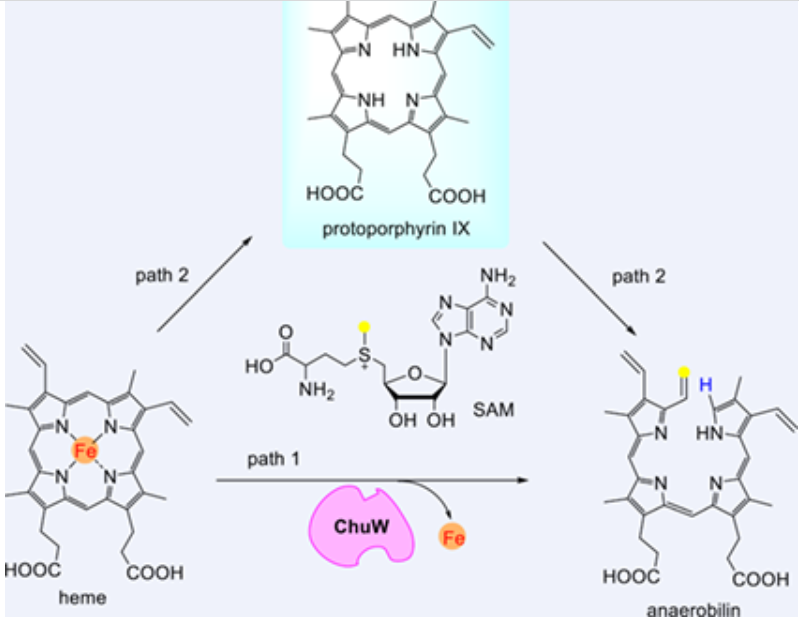
Demetallation of heme to release iron is a chemical difficult reaction and is highly rare in biochemistry, with apoferritin as the only known enzyme responsible for this process. Here we show the heme degradation enzyme ChuW catalyzes heme demetallation besides its known methyltransferase activity (which converts heme to a ring-open product anaerobilin).
We show the demetallation activity of ChuW is radical SAM-dependent, and likely involves the same set of intermediates involved in the anaerobilin-producing pathway. The ChuW-catalyzed demetallation reaction does not require external reductant, and can occur on several heme analogs with different metal centers. These findings establish a brand-new chemistry in the radical SAM enzymes, highlighting the remarkable catalytic diversity of this superfamily of enzymes.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25