(Peer-Reviewed) Finite element simulation of real cavity closure in cast Ti6Al4V alloy during hot isostatic pressing
Qian Xu 徐倩 ¹, Wen Li 李文 ¹, Ya-jun Yin 殷亚军 ¹, Jian-xin Zhou 周建新 ¹, Hai Nan 南海 ²
¹ State Key Laboratory of Materials Processing and Die and Mould Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074, China
中国 武汉 华中科技大学材料成形与模具技术国家重点实验室
² AECC Beijing Institute of Aeronautical Materials, Beijing, 100095, China
中国 北京 中国航发北京航空材料研究院
Abstract
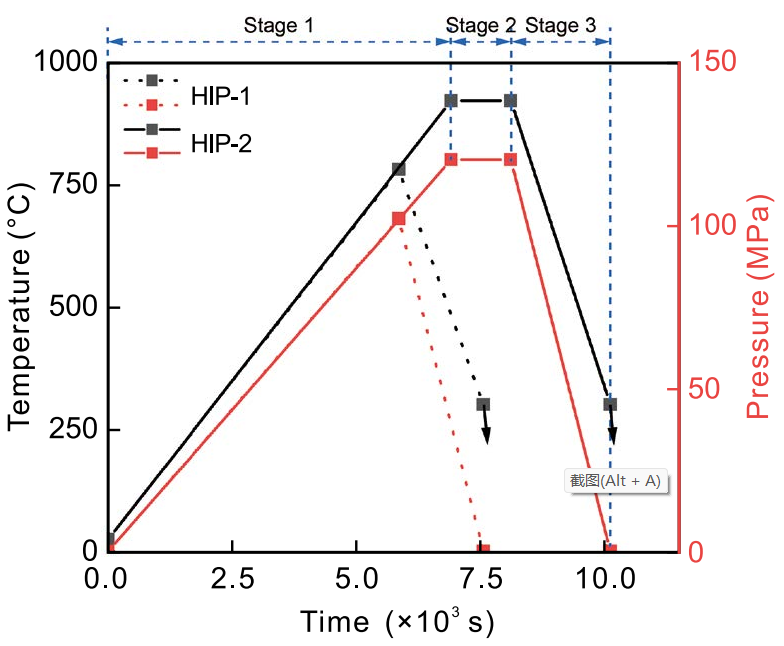
The healing behavior of shrinkage cavity inside the cast Ti6Al4V alloy during hot isostatic pressing (HIP) was investigated experimentally by interrupted hot isostatic pressing tests. The X-ray micro computed tomography was used to record the morphology changes before and after hot isostatic pressing.
The two-dimensional geometry obtained by the microCT scan was used in simulation to study the evolution of the real shrinkage cavity during hot isostatic pressing. Shrinkage cavities, shrinkage porosity and small gas pores can be effectively eliminated under proper HIP conditions. The two-dimensional morphology in the simulation results agrees well with the experimental results.
This study reveals that plastic deformation, creep and diffusion are the main mechanisms of cavity closure during hot isostatic pressing. In addition, the simplified elliptical pores with aspect ratios at different positions were used to replace the real pores to further study the factors affecting the position of dimples after HIP by simulation. It is found that the position of the dimples mainly depends on the aspect ratio of the elliptical pore and the distance between the pore surface and the external surface of the geometric model.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25