(Peer-Reviewed) Investigation of mechanical and diffusion properties in bcc Ti−Nb−Zr−Sn alloys via a high-throughput method
Zhu-hao WEN 闻祝浩 ¹, Yao WANG 王瑶 ², Wei-min CHEN 陈伟民 ¹, Li-jun ZHANG 张利军 ³, Yong DU 杜勇 ³
¹ Institute of Advanced Wear & Corrosion Resistant and Functional Materials, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
中国 广州 暨南大学先进耐磨蚀及功能材料研究院
² Centre of Excellence for Advanced Materials, Dongguan 523808, China
中国 东莞 东莞材料基因高等理工研究院
³ State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
中国 长沙 中南大学粉末冶金国家重点实验室
Abstract
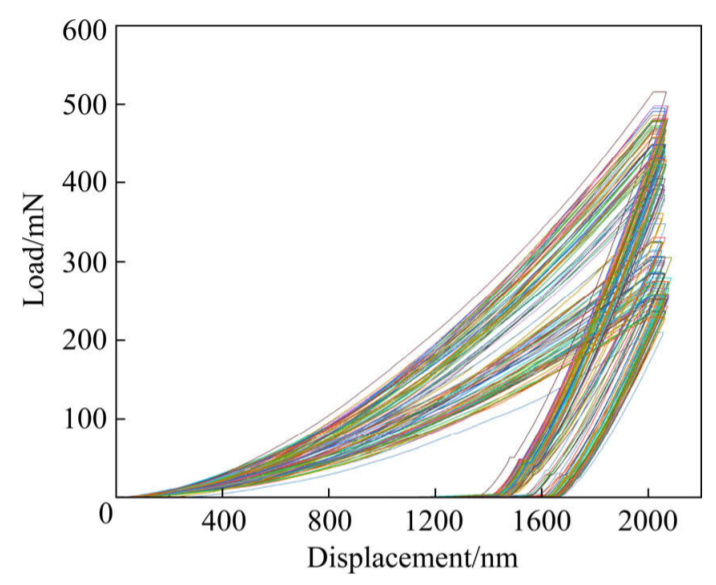
The mechanical and diffusion properties of bcc Ti−Nb−Zr−Sn alloys in the Ti-rich corner were analyzed through a high-throughput method with the combination of nanoindentation and diffusion couple techniques.
Nine groups of quaternary Ti−Nb−Zr−Sn diffusion couples were prepared after annealing at 1273 K for 25 h. The composition-dependent mechanical properties were determined by nanoindentation and electron probe microanalysis (EPMA) techniques.
Moreover, the corresponding interdiffusion coefficients were confirmed from the composition gradients of the quaternary diffusion couples using a pragmatic numerical inverse method. A composition-dependent database on the mechanical and diffusion properties was utilized to discuss the processability during the hot working.
The results reveal that the solute elements Nb and Sn are strictly controlled to increase the hardness and wear resistance of Ti−Nb−Zr−Sn alloys, and the additional element Zr is mainly useful to improve the processability during the hot working.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25