(Peer-Reviewed) Paving continuous heat dissipation pathways for quantum dots in polymer with orange-inspired radially aligned UHMWPE fibers
Xuan Yang 杨烜 ¹, Xinfeng Zhang 张信峰 ¹, Tianxu Zhang 张天旭 ¹, Linyi Xiang 向霖屹 ¹, Bin Xie 谢斌 ², Xiaobing Luo 罗小兵 ¹
¹ School of Energy and Power Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
中国 武汉 华中科技大学能源与动力工程学院
² School of Mechanical Science and Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
中国 武汉 华中科技大学机械科学与工程学院
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2024-07-05
Abstract
Thermal management of nanoscale quantum dots (QDs) in light-emitting devices is a long-lasting challenge. The existing heat transfer reinforcement solutions for QDs-polymer composite mainly rely on thermal-conductive fillers. However, this strategy failed to deliver the QDs' heat generation across a long distance, and the accumulated heat still causes considerable temperature rise of QDs-polymer composite, which eventually menaces the performance and reliability of light-emitting devices.
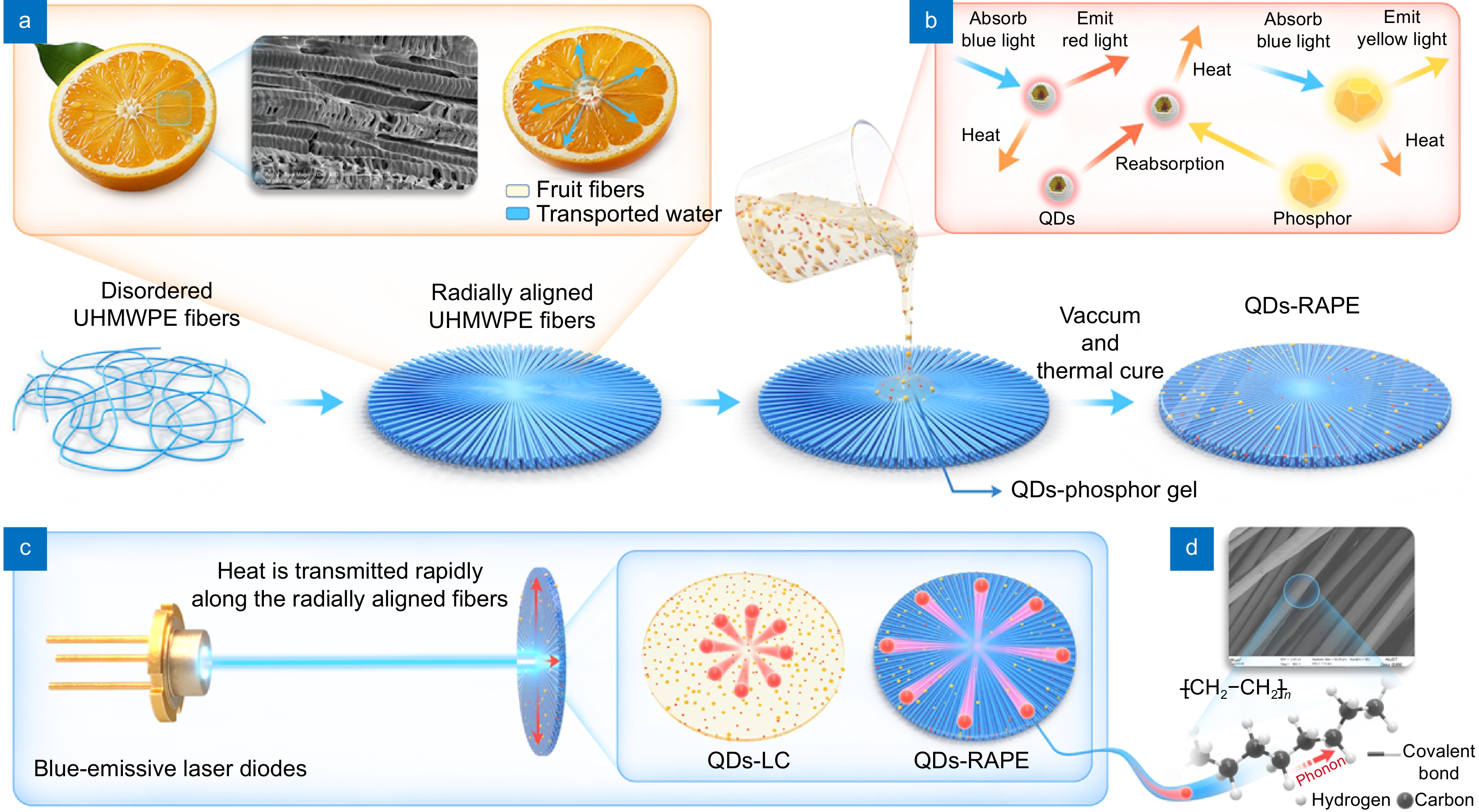
Inspired by the radially aligned fruit fibers in oranges, we proposed to eliminate this heat dissipation challenge by establishing long-range ordered heat transfer pathways within the QDs-polymer composite. Ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fibers (UPEF) were radially aligned throughout the polymer matrix, thus facilitating massive efficient heat dissipation of the QDs. Under a UPEF filling fraction of 24.46 vol%, the in-plane thermal conductivity of QDs-radially aligned UPEF composite (QDs-RAPE) could reach 10.45 W m⁻¹ K⁻¹, which is the highest value of QDs-polymer composite reported so far.
As a proof of concept, the QDs' working temperature can be reduced by 342.5 °C when illuminated by a highly concentrated laser diode (LD) under driving current of 1000 mA, thus improving their optical performance. This work may pave a new way for next generation high-power QDs lighting applications.
High-resolution tumor marker detection based on microwave photonics demodulated dual wavelength fiber laser sensor
Jie Hu, Weihao Lin, Liyang Shao, Chenlong Xue, Fang Zhao, Dongrui Xiao, Yang Ran, Yue Meng, Panpan He, Zhiguang Yu, Jinna Chen, Perry Ping Shum
Opto-Electronic Advances
2024-12-16
Ultra-high-Q photonic crystal nanobeam cavity for etchless lithium niobate on insulator (LNOI) platform
Zhi Jiang, Cizhe Fang, Xu Ran, Yu Gao, Ruiqing Wang, Jianguo Wang, Danyang Yao, Xuetao Gan, Yan Liu, Yue Hao, Genquan Han
Opto-Electronic Advances
2024-10-31