(Peer-Reviewed) Variations of widespread extreme cold and warm days in winter over China and their possible causes
Zhiyan Zuo 左志燕 ² ³, Mingqian Li 李明倩 ¹, Ning An 安宁 ¹, Dong Xiao 肖栋 ¹
¹ State Key Laboratory of Severe Weather, Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, Beijing, 100081, China
中国 北京 中国气象科学院 灾害天气国家重点实验室
² Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences/Institute of Atmospheric Sciences/IRDR-International Center of Excellence, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200348, China
中国 上海 复旦大学大气与海洋科学系 大气科学研究院 IRDR国际卓越中心
³ Collaborative Innovation Center on Forecast and Evaluation of Meteorological Disasters, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, 210044, China
中国 南京 南京信息工程大学气象灾害预报预警与评估协同创新中心
Abstract
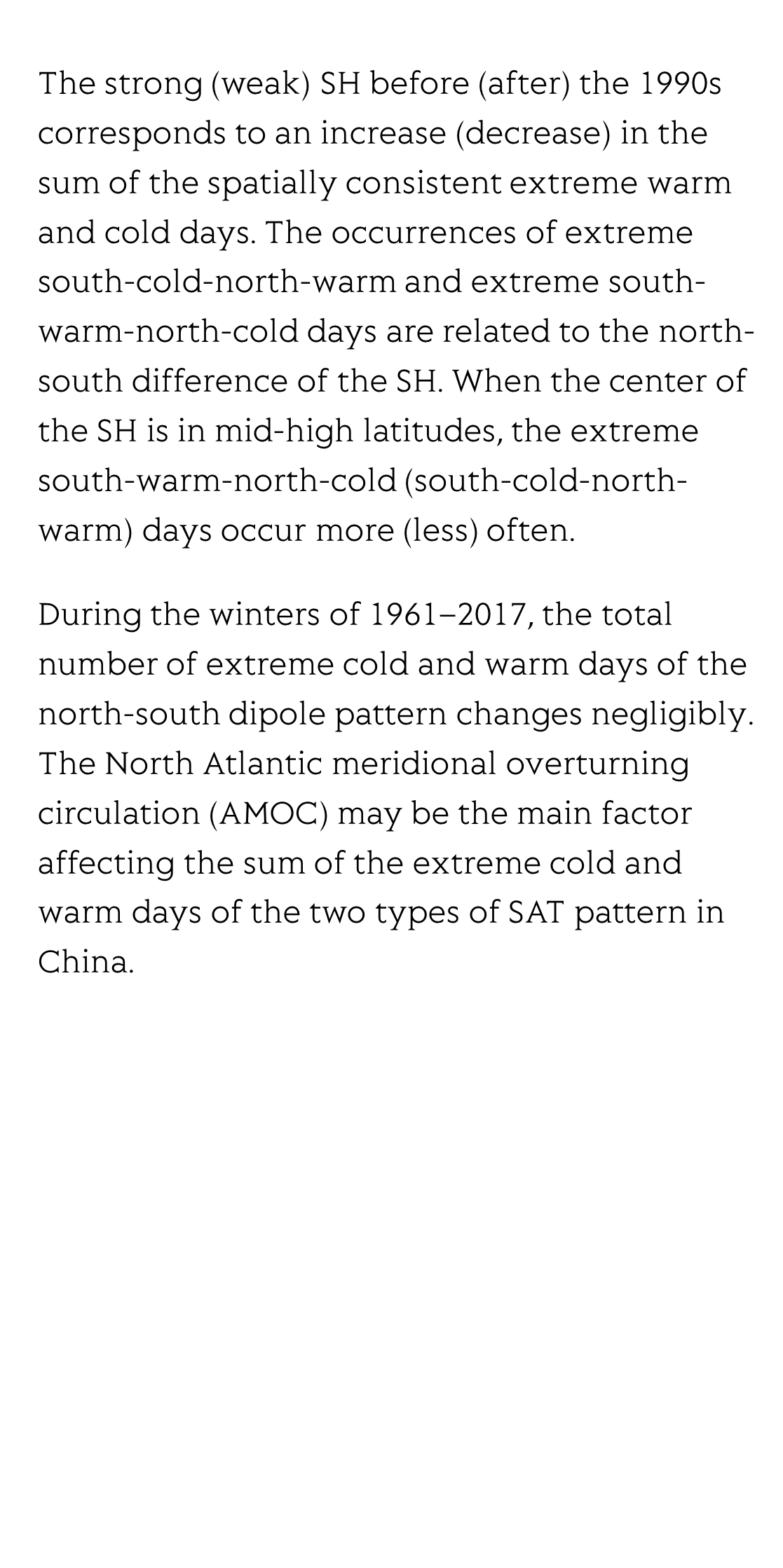
The two leading modes of winter surface air temperature (SAT) over China during 1961–2017 are a spatially consistent pattern and a north-south dipole pattern. Based on the two leading modes, the characteristics of the extreme cold and warm days in the two patterns, defined by the standard deviation larger than 1.28 or smaller than −1.28 in the time series of the two leading modes, are analyzed.
With the increase of winter SAT during 1961–2017, the number of spatially consistent extreme cold days decreased and their occurrence was restricted to late December to early January, whereas the number of spatially consistent extreme warm days increased significantly in January and February. Global warming is associated with an increase in the spatially consistent extreme warm days and a decrease in spatially consistent extreme cold days, but has little relation to the sum of extreme cold and warm days of either the spatially consistent or north-south dipole pattern. The Siberian High (SH) is the main factor controlling the sum of spatially consistent extreme warm and cold days.
The strong (weak) SH before (after) the 1990s corresponds to an increase (decrease) in the sum of the spatially consistent extreme warm and cold days. The occurrences of extreme south-cold-north-warm and extreme south-warm-north-cold days are related to the north-south difference of the SH. When the center of the SH is in mid-high latitudes, the extreme south-warm-north-cold (south-cold-north-warm) days occur more (less) often.
During the winters of 1961–2017, the total number of extreme cold and warm days of the north-south dipole pattern changes negligibly. The North Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) may be the main factor affecting the sum of the extreme cold and warm days of the two types of SAT pattern in China.
High-resolution tumor marker detection based on microwave photonics demodulated dual wavelength fiber laser sensor
Jie Hu, Weihao Lin, Liyang Shao, Chenlong Xue, Fang Zhao, Dongrui Xiao, Yang Ran, Yue Meng, Panpan He, Zhiguang Yu, Jinna Chen, Perry Ping Shum
Opto-Electronic Advances
2024-12-16
Ultra-high-Q photonic crystal nanobeam cavity for etchless lithium niobate on insulator (LNOI) platform
Zhi Jiang, Cizhe Fang, Xu Ran, Yu Gao, Ruiqing Wang, Jianguo Wang, Danyang Yao, Xuetao Gan, Yan Liu, Yue Hao, Genquan Han
Opto-Electronic Advances
2024-10-31