(Peer-Reviewed) Photo-driven fin field-effect transistors
Jintao Fu 付津滔 ¹ ², Chongqian Leng 冷重钱 ¹, Rui Ma 马睿 ¹ ³, Changbin Nie 聂长斌 ¹ ², Feiying Sun 孙飞莹 ¹, Genglin Li 李庚霖 ¹ ², Xingzhan Wei 魏兴战 ¹ ² ³
¹ Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing 400714, China
中国 重庆 中国科学院 重庆绿色智能技术研究院
² University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
中国 北京 中国科学院大学
³ Chongqing School, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing 400714, China
中国 重庆 中国科学院大学重庆学院
Opto-Electronic Science, 2024-05-28
Abstract
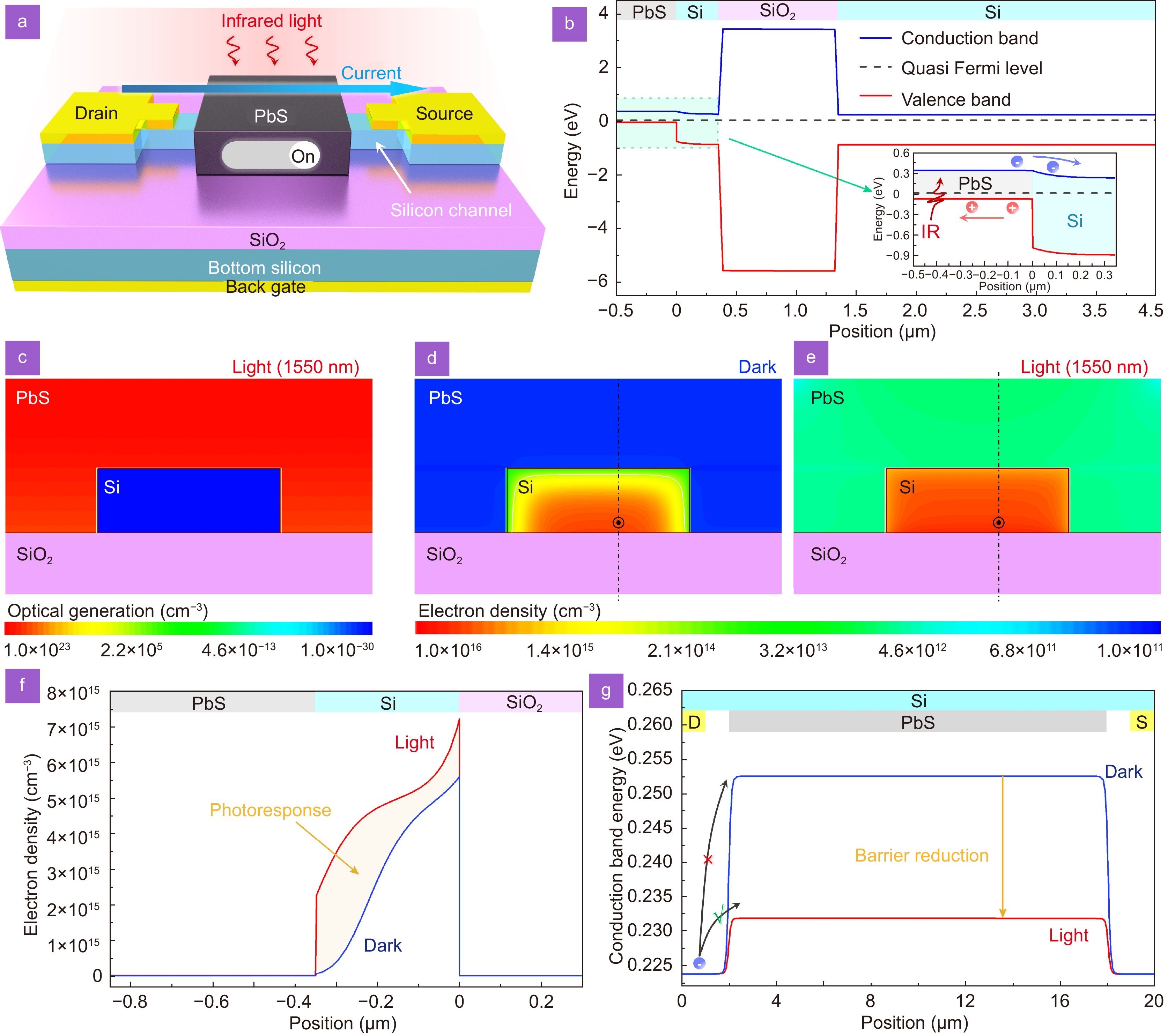
The integration between infrared detection and modern microelectronics offers unique opportunities for compact and high-resolution infrared imaging. However, silicon, the cornerstone of modern microelectronics, can only detect light within a limited wavelength range (< 1100 nm) due to its bandgap of 1.12 eV, which restricts its utility in the infrared detection realm. Herein, a photo-driven fin field-effect transistor is presented, which breaks the spectral response constraint of conventional silicon detectors while achieving sensitive infrared detection.
This device comprises a fin-shaped silicon channel for charge transport and a lead sulfide film for infrared light harvesting. The lead sulfide film wraps the silicon channel to form a “three-dimensional” infrared-sensitive gate, enabling the photovoltage generated at the lead sulfide-silicon junction to effectively modulate the channel conductance. At room temperature, this device realizes a broadband photodetection from visible (635 nm) to short-wave infrared regions (2700 nm), surpassing the working range of the regular indium gallium arsenide and germanium detectors.
Furthermore, it exhibits low equivalent noise powers of 3.2×10⁻¹² W·Hz⁻¹/² and 2.3×10⁻¹¹ W·Hz⁻¹/² under 1550 nm and 2700 nm illumination, respectively. These results highlight the significant potential of photo-driven fin field-effect transistors in advancing uncooled silicon-based infrared detection.
High-resolution tumor marker detection based on microwave photonics demodulated dual wavelength fiber laser sensor
Jie Hu, Weihao Lin, Liyang Shao, Chenlong Xue, Fang Zhao, Dongrui Xiao, Yang Ran, Yue Meng, Panpan He, Zhiguang Yu, Jinna Chen, Perry Ping Shum
Opto-Electronic Advances
2024-12-16
Ultra-high-Q photonic crystal nanobeam cavity for etchless lithium niobate on insulator (LNOI) platform
Zhi Jiang, Cizhe Fang, Xu Ran, Yu Gao, Ruiqing Wang, Jianguo Wang, Danyang Yao, Xuetao Gan, Yan Liu, Yue Hao, Genquan Han
Opto-Electronic Advances
2024-10-31