(Peer-Reviewed) Highly efficient emission and high-CRI warm white light-emitting diodes from ligand-modified CsPbBr3 quantum dots
Dongdong Yan 鄢冬冬 ¹, Shuangyi Zhao 赵双易 ¹, Yubo Zhang 张玉波 ², Huaxin Wang 王华昕 ¹, Zhigang Zang 臧志刚 ¹
¹ Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems (Ministry of Education), Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
中国 重庆 重庆大学 光电技术及系统教育部重点实验室
² Department of Physics, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
中国 深圳 南方科技大学物理系
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2022-01-25
Abstract
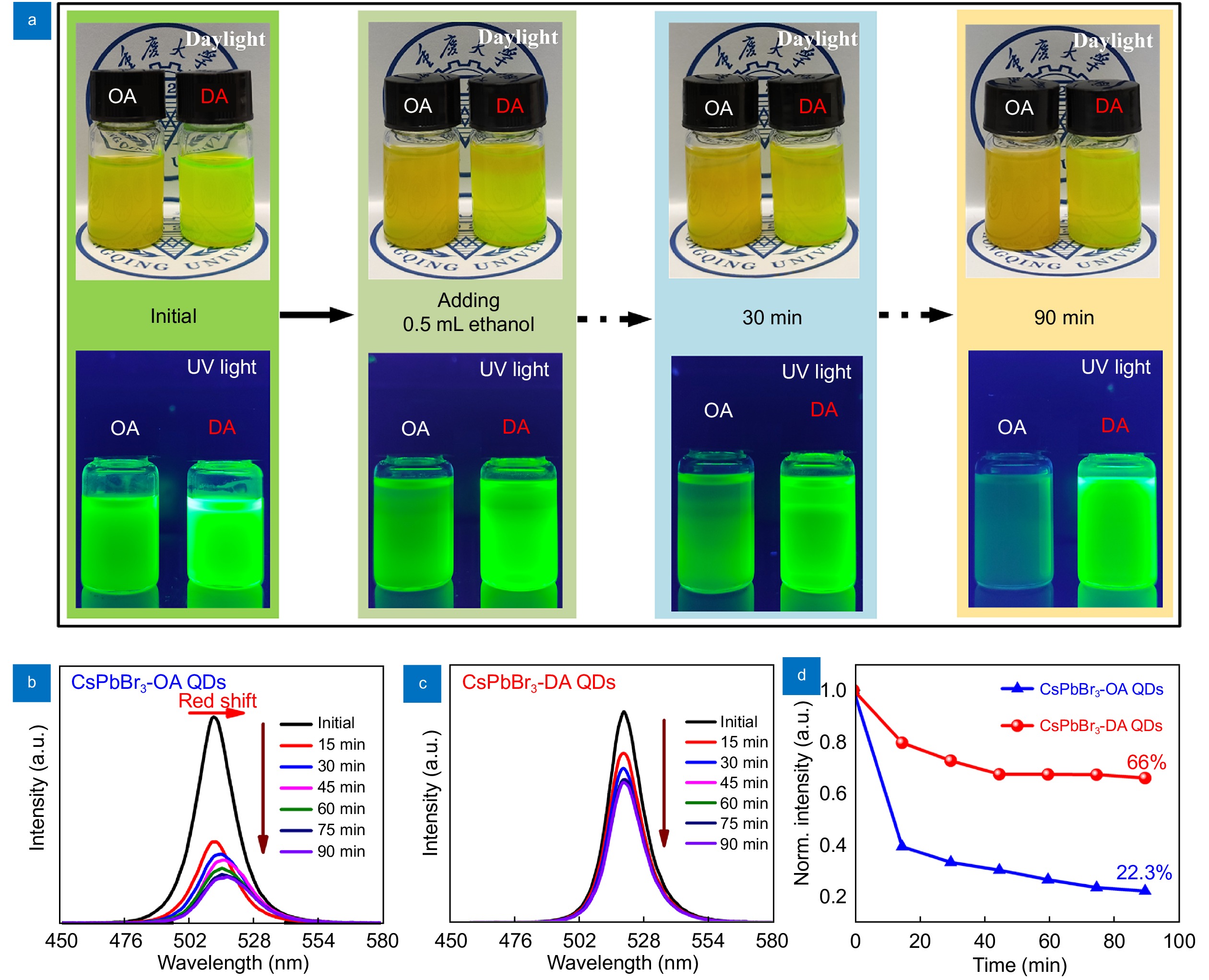
All-inorganic CsPbBr₃ perovskite quantum dots (QDs) have received great attention in white light emission because of their outstanding properties. However, their practical application is hindered by poor stability. Herein, we propose a simple strategy to synthesize excellent stability and efficient emission of CsPbBr₃ QDs by using 2-hexyldecanoic acid (DA) as a ligand to replace the regular oleic acid (OA) ligand.
Thanks to the strong binding energy between DA ligand and QDs, the modified QDs not only show a high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) of 96% but also exhibit high stability against ethanol and water. Thereby warm white light-emitting diodes (WLEDs) are constructed by combining ligand modified CsPbBr₃ QDs with red AgInZnS QDs on blue emitting InGaN chips, exhibiting a color rendering index of 93, a power efficiency of 64.8 lm/W, a CIE coordinate of (0.44, 0.42) and correlated color temperature value of 3018 K.
In addition, WLEDs based on ligand modified CsPbBr₃ QDs also exhibit better thermal performance than that of WLEDs based on the regular CsPbBr₃ QDs. The combination of improved efficiency and better thermal stability with high color quality indicates that the modified CsPbBr₃ QDs are ideal for WLEDs application.
High-resolution tumor marker detection based on microwave photonics demodulated dual wavelength fiber laser sensor
Jie Hu, Weihao Lin, Liyang Shao, Chenlong Xue, Fang Zhao, Dongrui Xiao, Yang Ran, Yue Meng, Panpan He, Zhiguang Yu, Jinna Chen, Perry Ping Shum
Opto-Electronic Advances
2024-12-16
Ultra-high-Q photonic crystal nanobeam cavity for etchless lithium niobate on insulator (LNOI) platform
Zhi Jiang, Cizhe Fang, Xu Ran, Yu Gao, Ruiqing Wang, Jianguo Wang, Danyang Yao, Xuetao Gan, Yan Liu, Yue Hao, Genquan Han
Opto-Electronic Advances
2024-10-31